August 15, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's and . have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
preprint
trusted source
proofread
Helium escapes from the atmosphere of a nearby exoplanet, observations find
Astronomers from the University of Chicago and elsewhere report the detection of an outflowing helium from the atmosphere of a nearby mini-Neptune exoplanet known as TOI-2134 b. The finding was detailed in a research paper published August 3 on the pre-print server arXiv.
Atmospheric escape is a process during which atmospheric gas leaves the planet's gravitational source and disperses into space. This process fundamentally shapes the properties of exoplanets.
Observations show that atmospheric escape occurs in a few nearby exoplanet systems, from hot Jupiters to lower-mass super-Earths/mini-Neptunes. However, in hot Jupiters, the mass-loss rates are not high enough to affect their evolution, but in the case of lower mass planets, atmospheric escape drives and controls their evolution.
Exoplanets with substantial hydrogen/helium atmospheres, due to extreme irradiation levels in their atmospheres, undergo hydrodynamic atmospheric escape. It is a thermal atmospheric escape mechanism leading to the escape of heavier atoms of a planetary atmosphere through numerous collisions with lighter atoms.
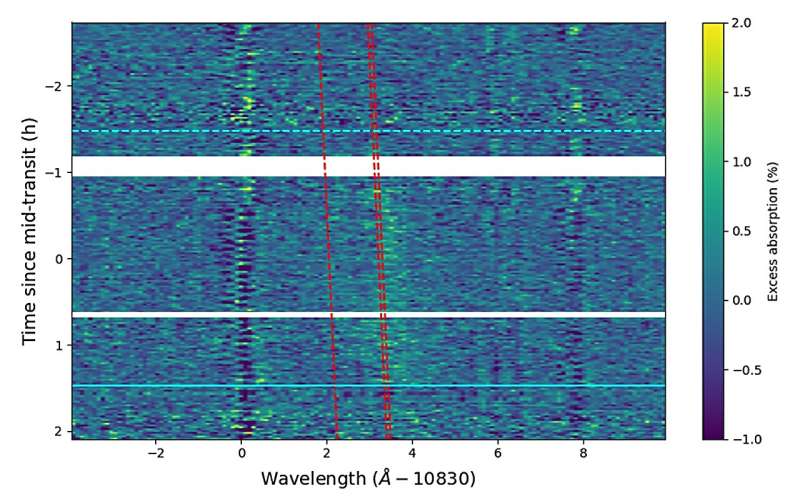
Now, a team of astronomers led by Michael Zhang has detected the atmospheric escape of helium from TOI-2134 b—a mini-Neptune located some 73.8 light years away from the Earth. The discovery was made with the Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRSPEC) mounted on the Keck II Telescope on Mauna Kea, Hawaii.
"In this paper, we present the first detection of escaping helium from TOI-2134 b, a warm mini-Neptune orbiting a nearby (23 pc) X-ray-quiet K dwarf," the researchers wrote.
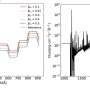
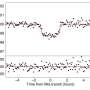
The observations found that the helium signal has an equivalent width of only 3.3 mÃ…, making TOI-2134 b the planet with the smallest helium signal among the ones with detected helium. In the absorption spectrum, the peak value was measured to be 0.37% and occurs at a redshift of 7 km/s. It also shows a secondary peak with a 10 km/s redshift and a peak absorption of 0.13%.
The study detected in TOI-2134 b a strong correlation between the energy-limited mass loss rate and the observationally inferred mass loss rate. It also turned out that TOI-2134 b experiences the lowest extreme ultraviolet (XUV) flux among the known exoplanets with helium in their atmospheres.
By analyzing the results, the astronomers concluded that the atmospheric escape of helium in TOI-2134 b is most likely due to photoevaporation by stellar XUV, disfavoring the core-powered mass loss mechanism. The results also suggest a mass loss timescale in the order of billions of years.
The researchers encourage further observations of TOI-2134 b and other mini-Neptunes with helium outflows, orbiting mature stars. They hope that such studies will help us better understand the nature of atmospheric escape occurring in alien worlds.
More information: Michael Zhang et al, Outflowing helium from a mature mini-Neptune, arXiv (2023).
Journal information: arXiv
© 2023 Science X Network