This article has been reviewed according to Science X's and . have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
In a fusion device plasma, a steep ion temperature gradient slows the growth of magnetic islands

Future fusion power plants will require good plasma confinement to sustain reactions and generate energy. One way to contain plasma for fusion reactions is to use a tokamak, a device that applies magnetic fields to "bottle" plasma. However, magnetic islands, a type of instability in the plasma, can destroy the confining magnetic field if they grow large enough.
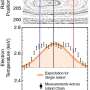
Researchers at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility have found that contrary to the flattened electron temperature profile, the ion temperature profile exhibited a steep change across islands. The study is in the journal Â鶹ÒùÔºical Review Letters.
Magnetic islands are instabilities in plasma that can grow until they result in a loss of confinement, and this sudden release of energy can damage the inner wall of a tokamak. The electron temperature profile is known to flatten within islands, with this change supporting island growth, but ion temperature has never been measured in an island.
The recent work on the tokamak at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility performed the first measurement of this parameter. The results indicate that ion temperature exhibits a steep gradient in the center of magnetic islands.
To understand this gradient, an international team of researchers performed a series of simulations. The steep ion temperature change was explained by reduced Drift-Kinetic Neoclassical Tearing Mode (NTM) simulations. The researchers found that within an island, ions form "drift island" structures that shift from the island, restoring ion temperature. These results will be used in a physical model of island destabilization and help constrain the Drift-Kinetic magnetic island onset model, which will provide key information for ITER and fusion power plant design.
This research on magnetic islands provides insights into how islands affect plasma stability. Researchers expect to see islands large enough to cause loss of confinement in tokomak devices such as ITER, the international experiment now under construction in France, and future fusion power plants. Therefore, researchers need accurate modeling and prediction of destabilization caused by islands.
This understanding will help researchers develop fusion device operating conditions that avoid islands. It will also help improve plasma modeling and the design of future devices.
More information: L. Bardóczi et al, Perturbed Ion Temperature and Toroidal Flow Profile Measurements in Rotating Neoclassical Tearing Mode Magnetic Islands, Â鶹ÒùÔºical Review Letters (2024).
Journal information: Â鶹ÒùÔºical Review Letters
Provided by US Department of Energy