This article has been reviewed according to Science X's and . have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
EPA's crackdown on power plant emissions is a big first step—but it will be hard to ensure captured carbon stays put
The U.S. government is on power plants' greenhouse gas emissions, and, as a result, a lot of money is about to pour into technology that can capture carbon dioxide from smokestacks and lock it away.
That raises an important question: Once carbon dioxide is captured and stored, how do we ensure it stays put?
Power plants that burn fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, release a lot of carbon dioxide. As that CO₂ accumulates in the atmosphere, it traps heat near the Earth's surface, .
But if CO₂ emissions can be captured instead and , existing fossil fuel power plants could meet the proposed new federal standards and reduce their impact on climate change.
We carbon capture and storage technologies as a scientist and an engineer. One of us, , proposed a tenet more than two decades ago that is echoed in the proposed standards: For all carbon extracted from the ground, must be disposed of safely and permanently.
To ensure that happens, carbon capture and storage needs an effective certification system.
EPA's proposed carbon crackdown
The , announced by the Environmental Protection Agency on May 11, 2023, are based on performance standards for carbon dioxide releases. They aren't yet finalized, and they likely will face fierce legal challenges, but the industry is paying attention.
Power plant owners could meet the proposed standards in any number of ways, including by shutting down fossil fuel-powered plants and replacing them with renewable energy such as solar or wind.
For those planning to continue to burn natural gas or coal, however, capturing the emissions and storing them long term is the most likely option.
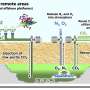
How CCS works for power plants
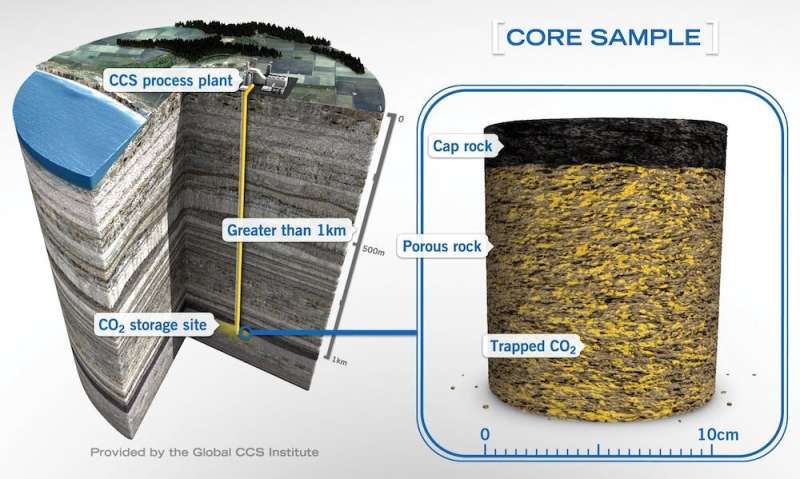
Carbon capture typically starts at the smokestack with " that can remove more than 90% of carbon dioxide emissions. The captured CO₂ is compressed and sent through pipelines for storage.
At most storage sites, CO₂ is injected , typically in porous rocks more than 3,300 feet (1,000 meters) below the surface.
Geologists look for sites with multiple layers of protection, including impermeable rock layers above the reservoir that can prevent gas from leaking out. In some sites, CO₂ chemically reacts with minerals and is eventually immobilized as a solid carbonate.
Carbon capture and storage is currently expensive, and developing the pipeline and storage infrastructure will likely take years. But as more CCS projects are built—helped by some in the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act—costs are likely to drop.
The Sleipner project in the North Sea has been putting away metric tons of CO₂ a year since 1996. In Iceland, CO₂ is injected into volcanic basalt rocks, where it reacts with the stone and rapidly .
In the U.S., companies have been injecting CO₂ into underground reservoirs for decades—initially, as a way to force more oil out of the ground. Today, these "enhanced oil recovery" projects can receive tax credits for the CO₂ that remains underground. As a result, some now inject more carbon into the ground than they extract as oil.
While there have been no notable CO₂ releases from geologic storage, that injection has to follow well-defined safety rules. Nothing is guaranteed.
That's why monitoring and certification are essential.
How to effectively certify carbon storage
The EPA has rules for CO₂ storage sites, but they are focused on protecting drinking water rather than the climate. Under , monitoring is required for all phases of the project and for 50 years after closing to check the safety of the groundwater and ensure that material injected underground does not contaminate it.
However, the current don't measure the amount of carbon stored, and the rules do not require that leaked carbon be replaced.
To provide more direction, we developed a designed to ensure that all carbon is stored safely and for the tens of thousands of years necessary to safeguard the climate.
We envision liability for the captured carbon dioxide shifting from the power plant owner to the storage site operator once the carbon dioxide is transferred. That would mean the storage site operator would be held liable for any leaks.
Under , a certificate authority would vet storage operators and issue certificates of carbon sequestration for stored carbon. These certificates could have market value if, as the EPA suggests, power plant operators are held responsible for the carbon stored. Future regulations could expand this requirement to other emitters, or simply demand that any carbon released is cleared by a corresponding certificate showing the same amount of carbon has been sequestered.
Careful monitoring, paired with certification that requires storage site owners to make up any losses, could help avoid and ensure that the investments meet the nation's climate goals.
Certification can be useful for carbon stored in any quantifiable storage reservoir, including trees, oceans and human infrastructure such as cement. We believe a that sets minimum requirements and responsibilities is necessary to assure that carbon is stored safely with a guarantee of permanence, regardless of how it is done.
Climate change will , and the federal government is putting to encourage development of carbon capture and storage sites. To avoid dubious methods, corner-cutting and greenwashing, carbon storage will have to be held to high standards. The U.S. can't afford to pin a large chunk of on carbon storage without proof.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from under a Creative Commons license. Read the .![]()