December 17, 2018 feature
Sub-picosecond photon-efficient imaging using single-photon sensors
Single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) are promising detector technologies that may be used to achieve active 3D imaging systems with fast acquisition, high timing accuracy and high detection sensitivity. Such systems have broad applications in the domains of biological imaging, remote sensing and robotics. However, the detectors face technical impairments known as pileup that cause measurement distortions to limit their precision. In a recent study, conducted at the Stanford University Department of Electrical Engineering, scientists Felix Heide and co-workers developed a probabilistic image formation model that could accurately model pileup. Using the proposed model, the scientists devised inverse methods to efficiently and robustly estimate the scene depth and reflectance from recorded photon counts. With the algorithm, they were able to demonstrate improvements to the accuracy of timing, compared to existing techniques. More importantly, the model allowed accuracy at the sub-picosecond in photon-efficient 3D imaging for the first time in practical scenarios, whereas previously only widely-varying photon counts were observed. The results are now published in Scientific Reports.
applications across disciplines that range from to of biological samples. Key requirements for these applications include high accuracy with timing, fast acquisition rates, dynamic operating ranges and high detection sensitivity to image objects hidden from a camera's view. Remote sensing and automated applications demand acquisition ranges from imaging relies on obtaining encoded information via the few returning photons of multiply scattered indirect light, in addition to the directly reflected light. To enable these applications, ultra-sensitive detectors were developed to record individual photons returning from a pulsed source of illumination. Single -photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) are one of the most sensitive time-resolved detector technologies that can be produced using the (CMOS) manufacturing process. The SPADs were rapidly established as a core detector technology for .
In its principle-of-function, SPADs are reverse-biased photodiodes that operate , i.e. above their breakdown voltage. When photons are incident on the active surface of a SPAD, a time stamped electron avalanche can be triggered. Repeated time stamping of photons returning from a synchronously pulsed illumination source that typically operate at MHz rates can accumulate a histogram of photon counts in time. The resulting histogram documents the approximate intensity of the returning light pulse to recover and characterize the distance, reflectance and 3D geometry of an object hidden from view.

Depending on the expected application, SPADs can operate in (that allows all photon events to be simultaneously detected at all arrival times) or (where only photons in a specific time window between pulses are detected). All applications are subject to a fundamental phenomenon known as that severely limits accuracy. Pileup can inherently limit the working principle of the SPAD detector. For example, after each triggered electron avalanche, the detector requires quenching prior to detecting further photon arrival events. During this 'dead time' (ten to hundreds of nanoseconds), the detector is inactive. This may result in the earlier photons of a single laser pulse triggering an avalanche, while later pulses are likely ignored in the dead time; creating inaccurate skewed measurements known as pileup. The phenomenon can be avoided by operating active imaging systems in a low-flux regime, as seen with used for first-photon imaging before.
However, conditions vary for 3D imaging applications in robotics, biological imaging or automotive sensing as they operate in environments where objects reflecting both high and low numbers of photons are essential for decision making. The large variance in acquired photon counts that results from diverse depths or the varying reflectivity of different objects is crucial for 3D imaging. In this work, Heide et al. introduced a new algorithm of estimation that overcame existing limitations of active 3D imaging systems using free running SPADs.
The proposed method improved the accuracy of the existing depth and estimation, across a wide range from low-flux to high-flux measurements. The scientists introduced a probabilistic image formation model that included pileup, with efficient inverse methods derived for depth and albedo estimations. The reconstruction framework jointly estimated all unknown parameters to overcome algorithmic limitations that previously restricted the timing precision. The proposed method allowed highly accurate and fast 3D imaging to open new operating regimes of photon-efficient 3D imaging applicable in conditions with dramatically varying photon counts.
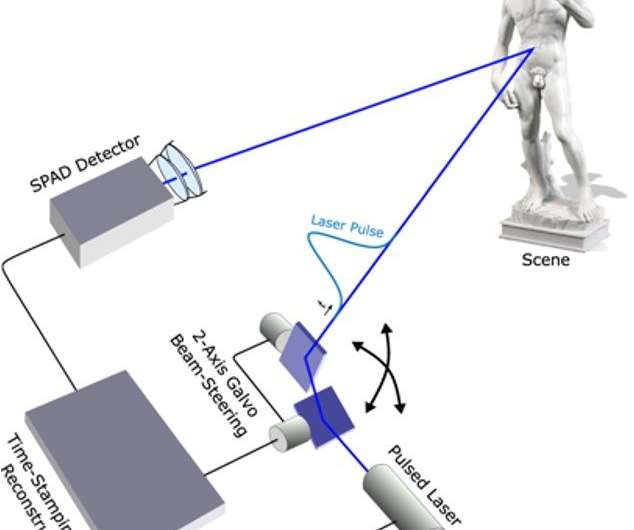
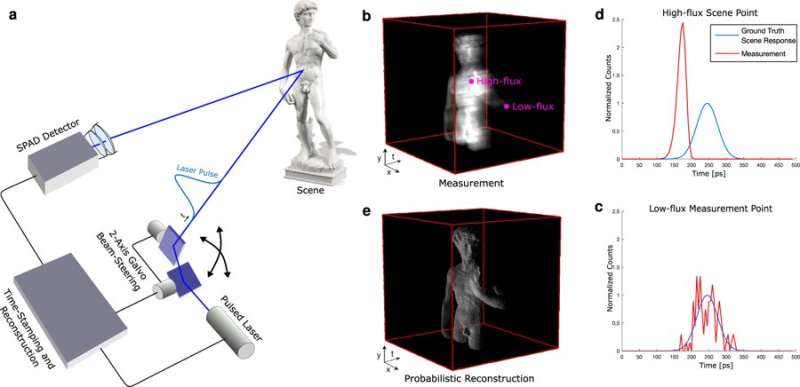
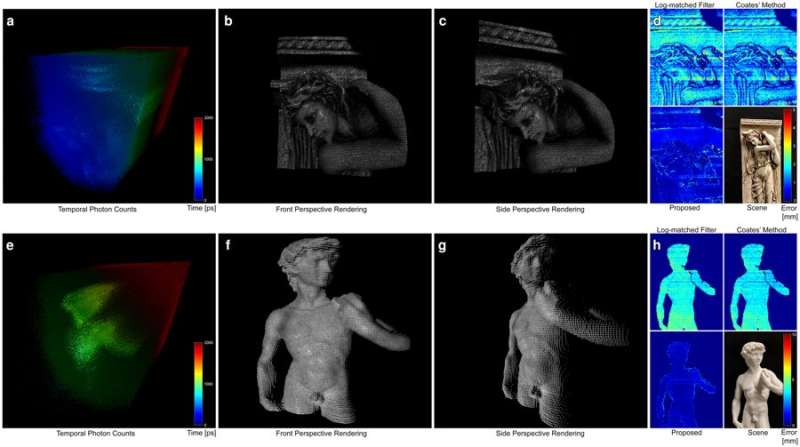
The performance of the proposed method was assessed on two scenes with highly varying reflectance and depth profiles, which included the Statue of David and a Bas-relief scene. Both instances contained objects with complex geometries and varying reflectance properties including specular behavior for the "Statue of David" and with spatially varying albedo in the 'Bas-relief" scene. For both scenes the scientists captured a ground truth reference measurement (information provided by empirical evidence) with a 5% neutral density filter, which eliminated pileup distortions by damping the source intensity.
The hardware of the system contained a time-resolved sensor, pulsed laser, illumination and collection optics. The setup also had a set of scanning mirrors to achieve a raster scan illumination pattern. The timing of photon arrivals was captured with a PicoHarp 300 time-correlated single photon counting module. The illumination source was a 450 nm or 670 nm picosecond laser (generating full width at half maximum FWHM, pulse widths of 90 ps and 50 ps). The collection optics consisted of a 75 m objective lens, 30 mm relay lens and a microscope objective, designed to extend the field of view of the SPAD across the area scanned by the source of illumination.
The experimental measurements served as input for the proposed method and were acquired without any filters in the optical path. Depth and albedo reconstructions along with corresponding error maps were obtained during the study. The results verified that the proposed method achieved high-quality reconstructions unaffected by scene-dependent pileup or shot noise (electronic noise associated with the particle nature of light). The results were compared to conventional methods, such as the and method that did not as effectively suppress pileup and suffered from scene-dependent depth precision. In contrast, the method introduced by Heide et al. achieved sub-picosecond accuracy.
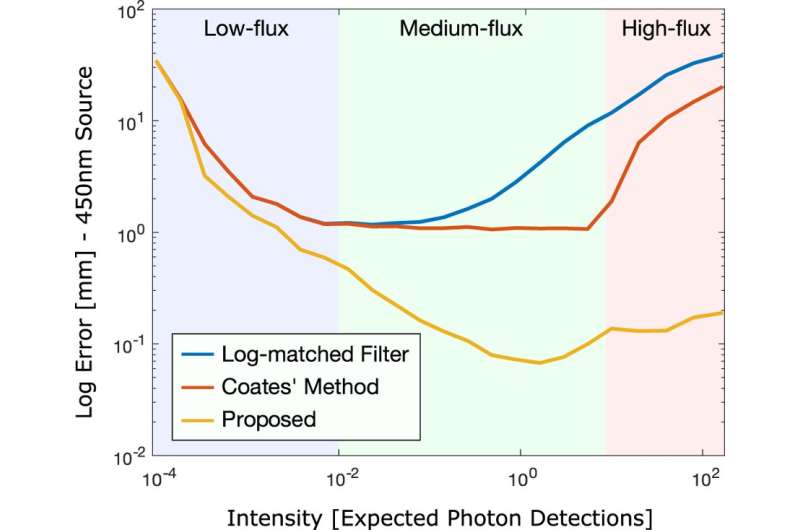
The code and data used by Heide et al. to generate the findings of the study will be . In total, the proposed probabilistic image formation model and corresponding inverse methods attained sub-picosecond accuracy for active 3D imaging, despite the laser pulse widths being larger than 50 ps. The novel method achieved high precision across a dynamic range from low-flux to high-flux measurements compared to traditional techniques. In the future, the proposed method can facilitate long-range acquisition by multiplexing multiple pileup affected responses. The proposed innovation paves the way for fast and precise photon-efficient 3D imaging systems, where widely varying photon counts are observed in practice. Applications can range across broad disciplines to include 3D mapping and navigation, art reconstruction and conservation, autonomous driving, vision for robots and machines, geographic information, industrial and microscopic imaging.
More information: 1. Sub-picosecond photon-efficient 3D imaging using single-photon sensors , Felix Heide et al, 07 December 2018, Scientific Reports.
2. Mapping the world in 3D , Brent Schwarz, July 2010, Nature Photonics.
3. The correction for photon 'pile-up' in the measurement of radiative lifetimes , P B Coates, February 1968, Journal of Â鶹ÒùÔºics E: Scientific Instruments, IOP Science.
4. Photon-Efficient Computational 3-D and Reflectivity Imaging with Single-Photon Detectors , S. Dongeek et al, July 2015, IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging.
Journal information: Scientific Reports , Nature Photonics , Science
© 2018 Science X Network